ARP poisoning & on-path
ARP protocol, or Address Resolution Protocol (ARP), is the technology responsible for allowing devices to identify themselves on a network. Address Resolution Protocol Poisoning (also known as ARP Spoofing or Man In The Middle (MITM) attack) is a type of attack that involves network jamming/manipulating by sending malicious ARP packets to the default gateway. The ultimate aim is to manipulate the “IP to MAC address table” and sniff the traffic of the target host.
There are a variety of tools available to conduct ARP attacks. However, the mindset of the attack is static, so it is easy to detect such an attack by knowing the ARP protocol workflow and Wireshark skills.
ARP analysis in a nutshell:
Works on the local network
Enables the communication between MAC addresses
Not a secure protocol
Not a routable protocol
It doesn’t have an authentication function
Common patterns are request & response, announcement and gratuitous packets.
Questions
Use the Desktop/exercise-pcaps/arp/Exercise.pcapng file.
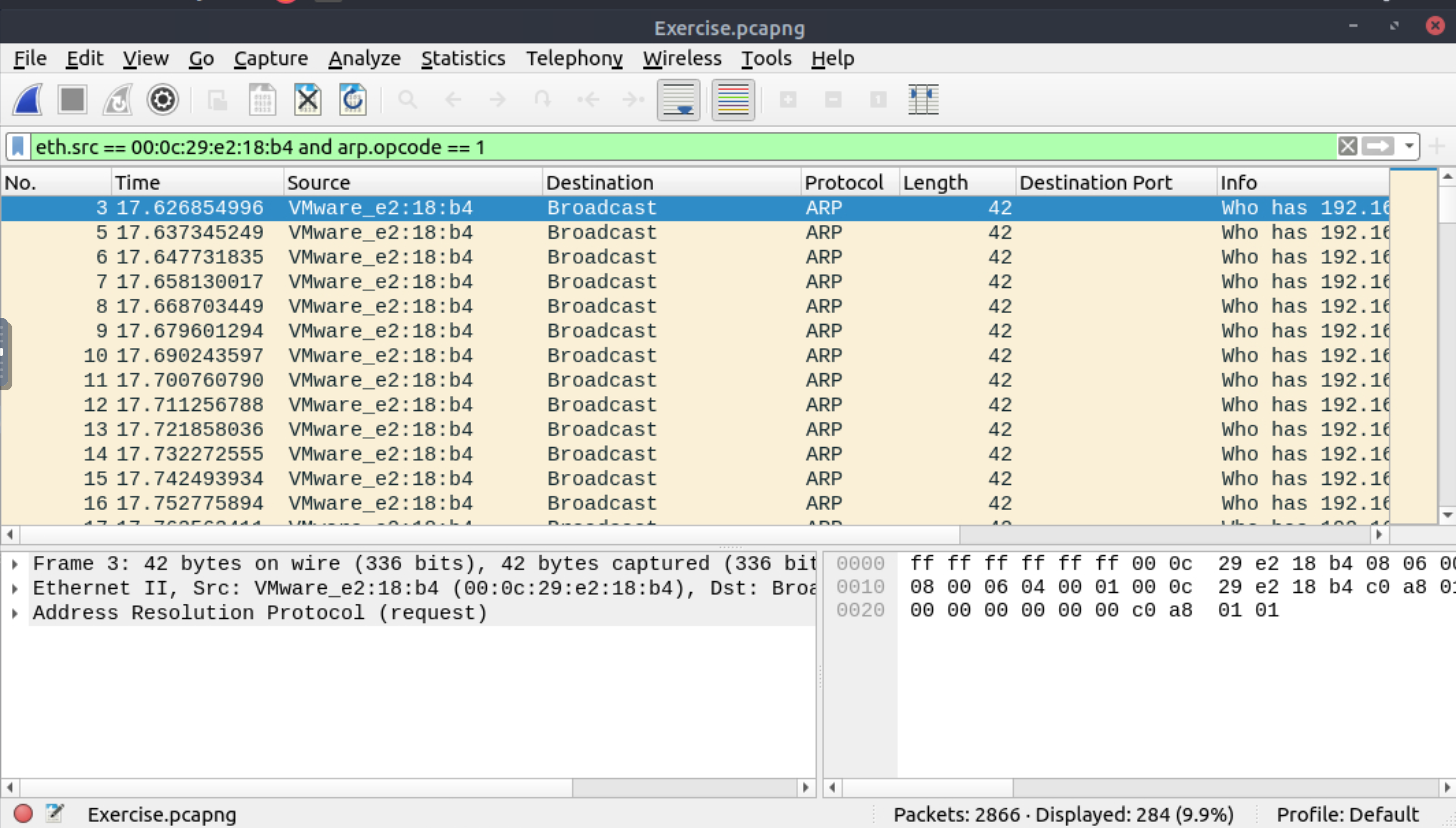
What is the number of ARP requests crafted by the attacker?
 |
|---|
284 |
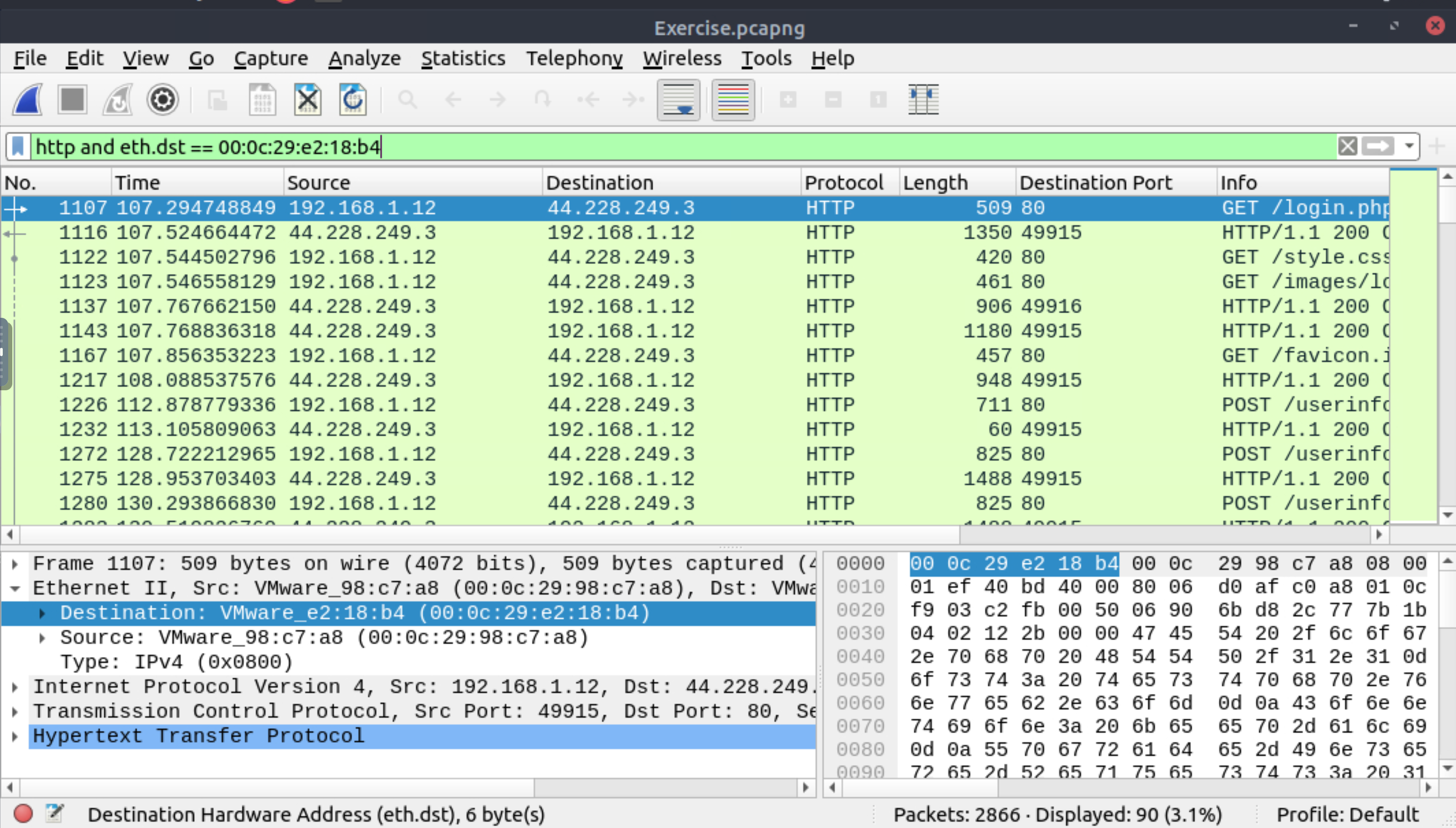
What is the number of HTTP packets received by the attacker?
 |
|---|
90 |
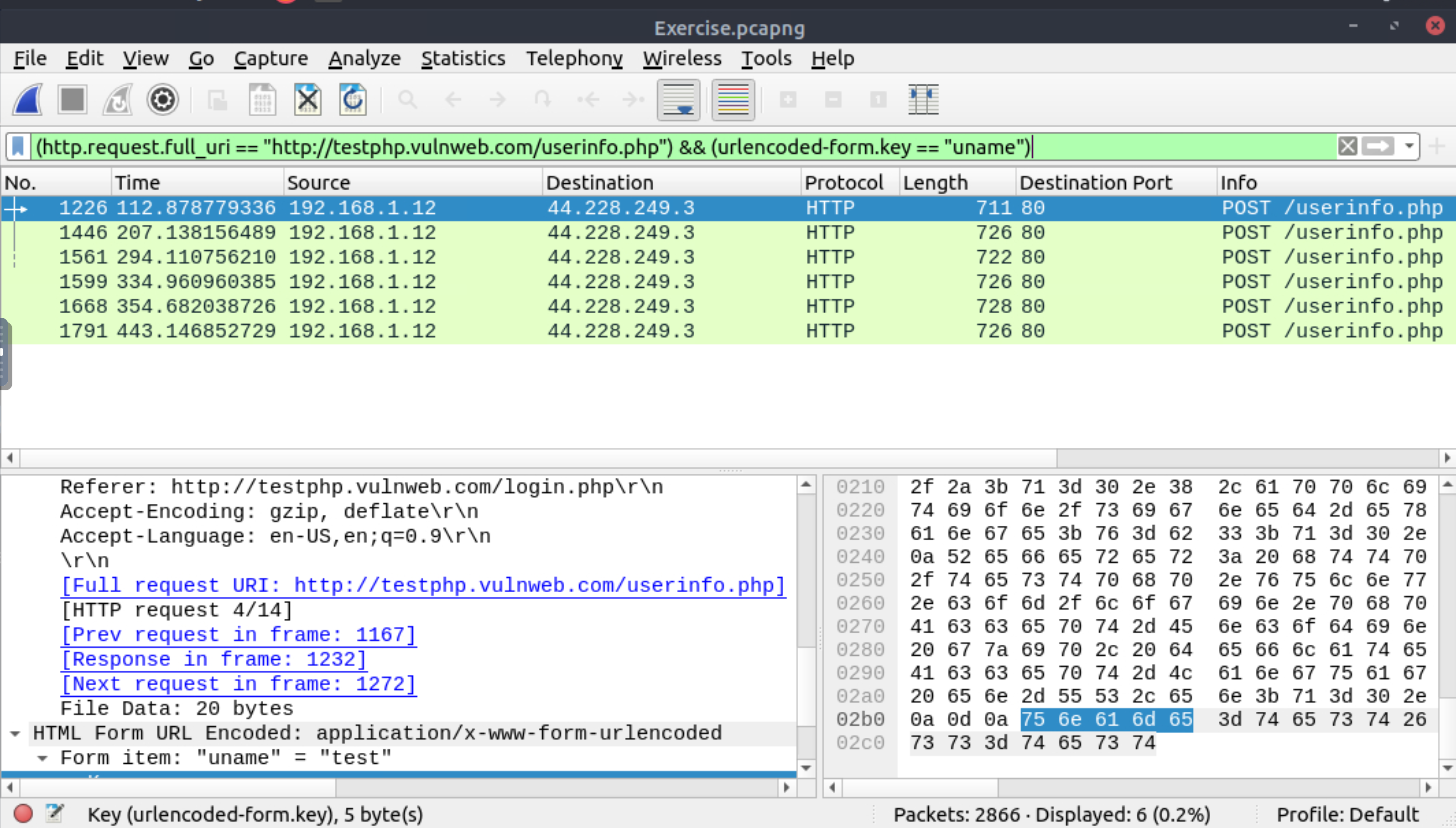
What is the number of sniffed username&password entries?
 |
|---|
6 |
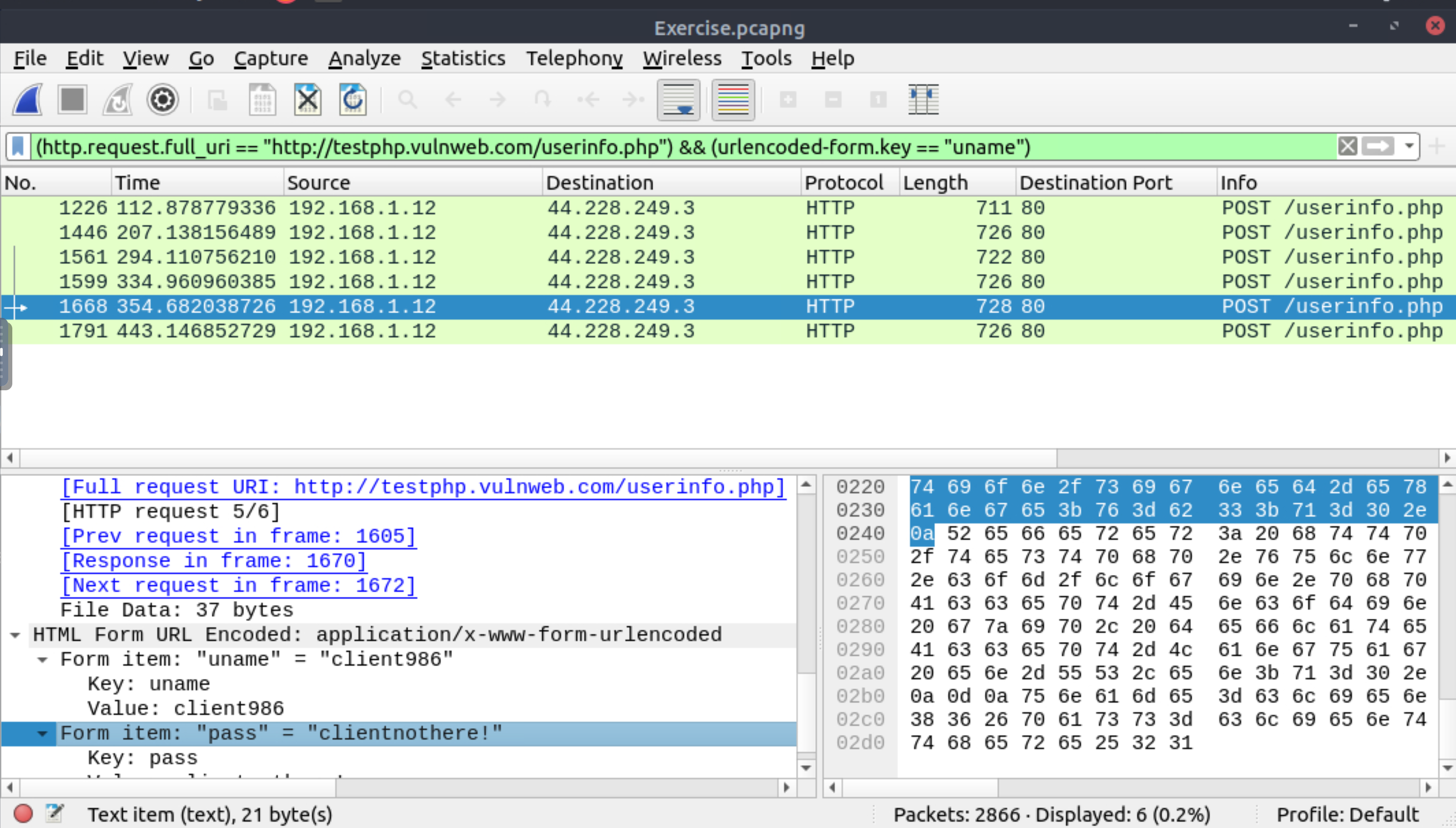
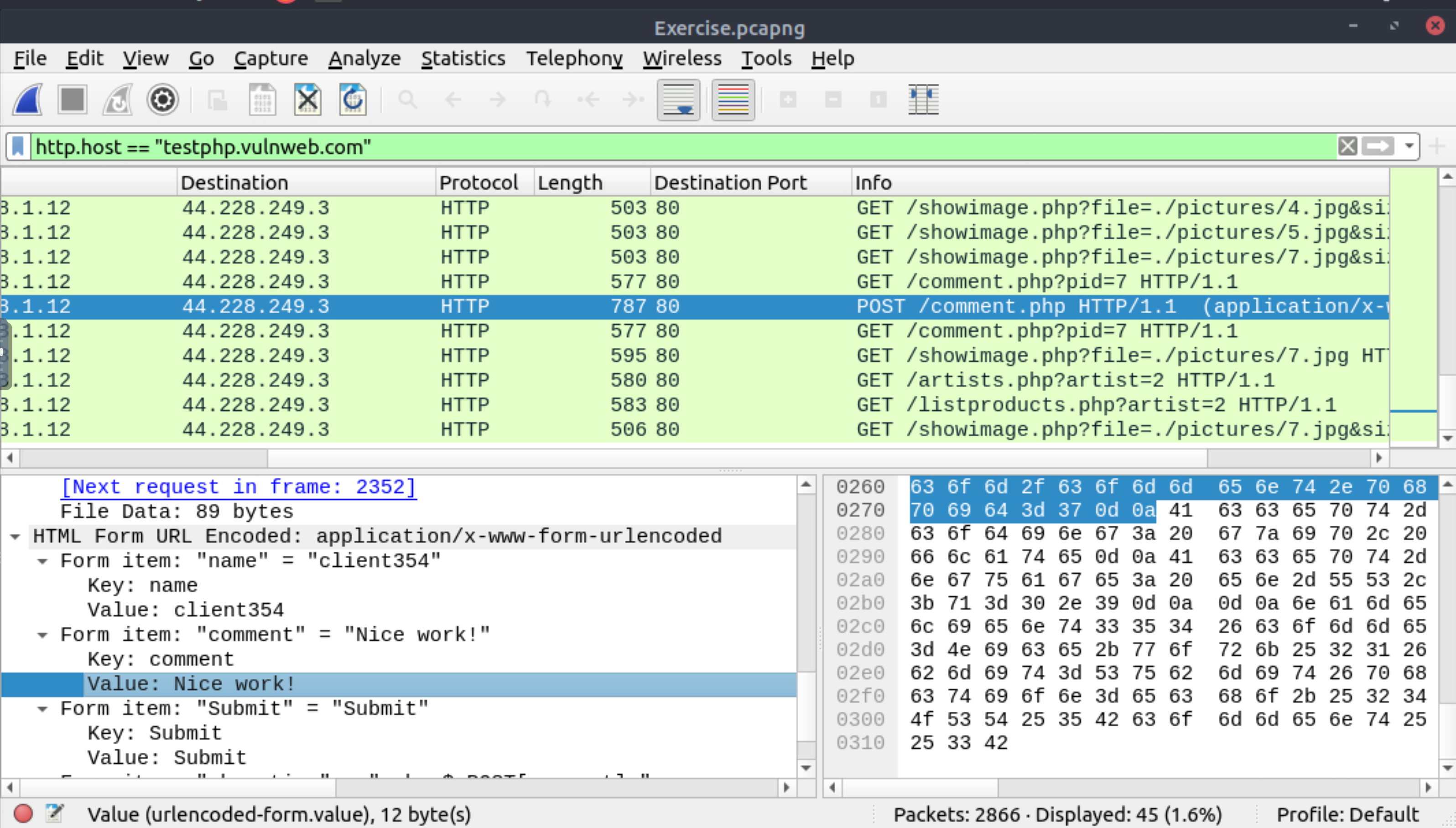
What is the password of the Client986?
 |
|---|
clientnothere! |
What is the comment provided by the Client354?
 |
|---|
Nice work! |
.